Epoxy Flooring — Ultimate Guide for Architects & Builders
From Basics to Architectural Details, Compliance Standards, and Design InsightsIntroduction
Epoxy flooring has evolved from an industrial solution into a versatile, design-driven system now seen in homes, retail, healthcare, education, and commercial environments. In Sydney, where climate, safety, and regulatory frameworks influence construction choices, epoxy systems offer a blend of durability, compliance, and design flexibility unmatched by many alternatives.
This guide aims to serve as a comprehensive resource for architects, designers, builders, and property owners. It addresses not only the chemistry and applications of epoxy flooring but also the regulatory requirements set out in Australian Standards, Work Health and Safety (WHS) legislation, and local building codes.
We provide professional epoxy flooring services for the Sydney metro area and around NSW. For more information about our services, please visit our Epoxy Flooring Sydney service page.
What is Epoxy Flooring?
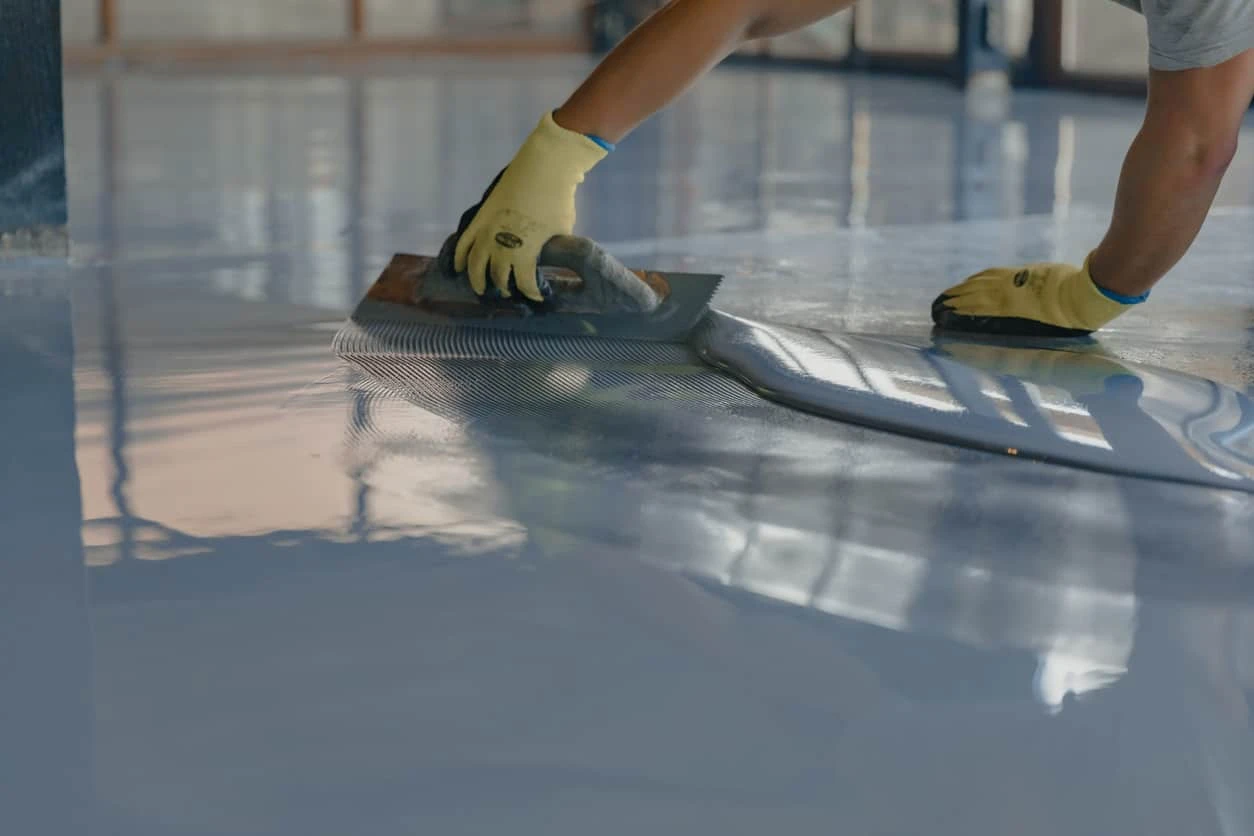
Epoxy flooring is a resin-based flooring system created by mixing epoxy resin with a curing agent (also called a hardener). The chemical reaction forms a thermoset polymer that bonds permanently with a prepared concrete substrate. Epoxy resin has very good adhesive properties and produces a seamless, dense surface with exceptional load-bearing capacity.
Epoxy coating systems can be applied in one, two, or multiple layers—primer, body coat, decorative coat, and topcoat—depending on performance requirements. This enables formulators and applicators to alter the layers of the applied coating system and enhance the end results. For instance, an epoxy coating system with enhanced resistance to water will be used as a primer to stop the moisture, and another epoxy system with high resistance against UV light and abrasion will be used as a top coat. That is how we can have systems such as self-leveling epoxy, flake systems, metallic finishes, quartz systems, and electrostatic-dissipative coatings (ESD Coatings) for sensitive environments. These are only some examples. However, you can design endless variations of epoxy coating systems tailored for each specific project’s needs and requirements.
Historical Development
Originally developed during the mid-20th century for industrial and military applications, epoxy resins were valued for their chemical resistance and adhesion. Over the past three decades, architectural innovation and decorative techniques have expanded their use into residential and commercial design.
Today, epoxy is considered a modern alternative to tiles, vinyl, and polished concrete. Its growth in Australia has been fuelled by rising awareness of hygienic requirements in commercial kitchens, WHS regulations in warehouses, and the demand for low-maintenance solutions in private garages.


Regulatory & Architectural Standards in Australia
For flooring in Sydney and across Australia, epoxy systems must align with architectural and regulatory standards:
3.1 Slip Resistance
- AS 4586:2013 (Slip Resistance Classification of New Pedestrian Surface Materials) governs slip ratings.
- Epoxy floors can be finished to meet R9–R13 classifications.
- For commercial kitchens, hospitals, and wet areas, higher slip ratings are mandatory.
👉 Reference: Standards Australia – AS 4586
3.2 Building Code of Australia (BCA)
- Epoxy flooring systems fall under Volume One – Building Code of Australia, particularly in commercial and industrial spaces.
- Compliance relates to fire resistance, slip resistance, and hygiene.
👉 Reference: Australian Building Codes Board
3.3 Work Health and Safety (WHS) Requirements
- Employers must provide safe flooring surfaces under the WHS Act 2011 (NSW).
- Epoxy’s slip-resistant and chemical-resistant properties make it suitable for compliance in warehouses and factories.
👉 Reference: SafeWork NSW
3.4 Food Safety Standards
- For commercial kitchen flooring and food handling facilities, epoxy must meet Food Standards Australia New Zealand (FSANZ) guidelines for seamless, easily cleanable flooring.
👉 Reference: FSANZ – Chapter 3 Food Safety Standards
Types of Epoxy Flooring Systems
Epoxy flooring can be customised for specific environments. Below is an overview relevant to Sydney architectural applications:
4.1 Self-Levelling Epoxy
- Smooth, seamless finish.
- Suitable for showrooms, offices, and homes.
4.2 Epoxy Flake Flooring
- Incorporates vinyl chips for decorative appeal.
- Popular in garages, schools, and retail spaces.
4.3 Metallic Epoxy
- Pigments create a marbled, 3D effect.
- Suited for high-end residential or boutique commercial environments.
4.4 High-Build & Industrial Epoxy Flooring
- Applied in thick layers (2–5mm).
- Resistant to forklifts, impacts, and chemicals.
- Common in warehouses, logistics hubs, and industrial kitchens.
4.5 Anti-Static (ESD) Epoxy
- Protects sensitive equipment.
Used in laboratories, cleanrooms, and electronic facilities.
4.6 Tough & Chemical Resistant
- Meant for heavy-duty use.
- Handle harsh demands: oil drips, grease slashes, heavy tool impact, and hydraulic lift pressure.
- Easy to clean and maintain.
Used in tool shops and mechanical workshops.

Architectural Details and Specifications
Architects specifying epoxy flooring must consider:
- Surface Preparation – Mechanical grinding to CSP 2–3 (Concrete Surface Profile) for adhesion.
- Moisture Testing – ASTM F2170 (in-situ RH testing) recommended; excessive slab moisture leads to failure.
- Joint Detailing – Expansion joints must be honoured to prevent cracking.
- Slip Ratings – Epoxy must meet AS 4586 slip resistance requirements.
- Thickness & Build – 2mm decorative vs 5–6mm industrial systems.
- UV Stability – Polyaspartic or polyurethane topcoats may be added in sun-exposed areas.
- Load Ratings – Industrial epoxy must withstand forklift loads and point loads >500kg.
👉 Reference: Cement Concrete & Aggregates Australia
Epoxy Flooring vs Alternative Flooring Options
| Flooring Type | Durability | Maintenance | Hygiene | Aesthetics | Cost (Sydney avg) |
| Epoxy | 10–20 years | Very low | Seamless, hygienic | Customisable | $40–$120/m² |
| Tiles | 10–15 years | Moderate (grout cleaning) | Joints = bacteria risk | Wide designs | $70–$150/m² |
| Vinyl | 7–10 years | Moderate | Seamless but lower chemical resistance | Limited | $40–$90/m² |
| Polished Concrete | 15+ years | Low | Seamless | Industrial look | $60–$120/m² |
Applications Across Sydney
7.1 Residential Garages
- Clean, dust-free, oil-resistant surfaces.
- Increasingly popular in North Shore and Northern Beaches homes.
7.2 Commercial Kitchens
- FSANZ-compliant, slip-resistant epoxy is now standard.
- Common in Sydney CBD restaurants and catering facilities.
7.3 Warehouses and Factories
- Line-marked epoxy assists with WHS compliance.
- Used in Western Sydney logistics hubs.
7.4 Retail and Hospitality
- Decorative metallic or flake finishes create brand identity.
- Seen in cafes across Inner West and Eastern Suburbs.
Installation Process (Best Practice)
- Concrete Grinding & Preparation
- Moisture & Crack Repair
- Primer Application
- Base Coat (epoxy resin)
- Decorative Layer (flakes, metallics, or quartz)
- Topcoat Application (UV, chemical resistant)
- Curing Period (48–72 hrs for traffic, 7 days for full cure)
👉 Reference: Concrete Institute of Australia
Cost Analysis in Sydney
- Basic Garage Systems: $40–$60 per m²
- Commercial Kitchens: $60–$90 per m²
- Decorative Metallics: $80–$120 per m²
- High-Build Industrial Systems: custom quotes
Costs are influenced by slab condition, repairs, surface prep, and design choices.
Maintenance and Lifecycle
- Sweep regularly to remove grit.
- Mop with pH-neutral cleaner.
- Avoid heavy solvent spills.
- Re-coat top layers every 8–10 years for aesthetics.
Lifecycle studies show epoxy outperforms vinyl and tiles in terms of whole-of-life cost efficiency.
👉 Reference: Sustainable Built Environment National Research Centre (SBEnrc)
Common Problems and How to Avoid Them
- Peeling/Delamination → caused by poor surface prep.
- Blistering → moisture vapour transmission.
- Discolouration → UV exposure (mitigated with polyaspartic topcoat).
- Hot Tyre Pickup in Garages → prevented by proper curing and topcoat.
Need Epoxy Flooring in Sydney?
Fast Quotes for Commercial, Industrial & Garage Epoxy Floors
Future of Epoxy Flooring
Trends in Australia include:
- Low-VOC epoxies for green building compliance.
- Recycled content fillers for sustainability.
- Hybrid polyaspartic systems for faster curing.
- Integration into Green Star rated buildings.
👉 Reference: Green Building Council of Australia

| Region | Percentage |
|---|---|
| APAC | 60% |
| EMEA | 23% |
| North America | 13% |
| Latin America | 4% |
Conclusion
Epoxy flooring has become a cornerstone of modern architecture and construction in Sydney, delivering durability, hygiene, compliance, and aesthetic flexibility. For architects and builders, epoxy provides a specification-friendly system that aligns with national standards and client demands. For homeowners and businesses, it delivers a cost-effective, long-lasting solution.
By understanding the technical, architectural, and regulatory dimensions of epoxy flooring, stakeholders can ensure their projects meet the highest standards of performance and safety.
📞 For project consultation, specifications, or site assessments, contact Epoxy Flooring Tech Sydney.